How to operate a drone safely and effectively is a question many ask before taking to the skies. This guide delves into the essential aspects of drone operation, from understanding regulations and safety protocols to mastering flight controls and capturing stunning aerial footage. We’ll cover everything from pre-flight checks and calibration to troubleshooting common issues and handling emergencies, ensuring you’re well-equipped for a safe and rewarding drone experience.
Whether you’re a complete beginner or looking to refine your skills, this comprehensive guide will provide the knowledge and confidence you need.
We will explore the intricacies of drone technology, explaining the function of each component and how they work together to enable flight. We will also provide practical advice on navigating legal requirements, ensuring your flights comply with local regulations and minimize potential risks. The journey from novice to confident pilot begins here.
Drone Regulations and Safety
Operating a drone responsibly requires understanding and adhering to both legal regulations and crucial safety procedures. Failure to do so can result in fines, legal repercussions, and potential harm to people and property. This section will cover essential aspects of safe and legal drone operation.
Drone Regulations by Country

Drone regulations vary significantly across countries. Understanding the specific laws of your operating location is paramount. These laws often dictate where you can fly, what permits are required, and the penalties for non-compliance. Here’s a comparison for three countries:
| Country | License Requirement | Flight Restrictions | Penalties |
|---|---|---|---|
| United States | Registration required for most drones; Part 107 license needed for commercial operation. | Restrictions near airports, crowded areas, and sensitive locations; maximum altitude limits. | Fines, license suspension, or even criminal charges. |
| United Kingdom | Registration required for most drones; Operational Certificate (A2 CofC) needed for commercial operations. | Restrictions on flying near airports, crowds, and certain buildings; altitude restrictions apply. | Fines, license suspension, or legal action. |
| Canada | Registration required for most drones; Basic and Advanced certificates for commercial and recreational operation, respectively. | Restrictions on flying near airports, people, and sensitive infrastructure; altitude and distance limits. | Fines and potential legal repercussions. |
Drone Safety Procedures
Safe drone operation involves a series of procedures before, during, and after flight. Careful planning and adherence to these steps significantly reduce the risk of accidents.
Pre-Flight Inspection Checklist
- Check battery levels and charge status.
- Inspect propellers for damage or wear.
- Verify GPS signal strength and accuracy.
- Ensure all components are securely attached.
- Test the drone’s motors and controls.
- Check for any obstacles in the flight area.
- Review weather conditions and avoid flying in strong winds or rain.
Potential Risks and Mitigation
Potential risks include collisions with objects or people, loss of control, battery failure, and damage to the drone itself. Mitigation strategies include thorough pre-flight checks, choosing appropriate flight locations, and practicing safe flying techniques.
Drone Parts and Functionality
Understanding the components of a drone is essential for both operation and troubleshooting. This section details the key parts and their functions.
Key Drone Components and Their Functions
A standard drone typically consists of a frame, motors, propellers, a flight controller, a battery, a GPS module, and a camera. The frame provides structural support, motors provide thrust, propellers generate lift, the flight controller manages flight stability, the battery provides power, the GPS module aids navigation, and the camera captures images and videos.
Drone Propellers and Flight Performance
Different propeller designs affect flight characteristics such as speed, efficiency, and maneuverability. Larger propellers generally provide more lift and slower speeds, while smaller propellers offer faster speeds but less lift. Propeller pitch also affects performance.
Drone Battery Types and Charging
Most drones utilize lithium polymer (LiPo) batteries. These batteries require careful handling and charging procedures. Overcharging or improper handling can lead to battery damage or even fire. Always follow the manufacturer’s instructions for charging and storage.
Drone Camera Features
Drone cameras vary significantly in resolution, sensor size, field of view, and features such as image stabilization and video recording capabilities. Higher-resolution cameras capture more detail, larger sensors perform better in low light, and wider field of view lenses capture broader scenes.
Drone Flight Controller Internal Workings (Diagram Description)
A diagram of a drone’s flight controller would show its central processing unit (CPU), inertial measurement unit (IMU), barometer, GPS receiver, and connections to the motors and other components. The CPU processes data from sensors to maintain stability and execute commands from the remote control. The IMU measures the drone’s orientation and movement, while the barometer measures altitude. The GPS provides location data for navigation.
All these components work together to provide stable and controlled flight.
Pre-Flight Setup and Calibration
Proper pre-flight setup and calibration are crucial for safe and successful drone operation. These steps ensure the drone functions correctly and provides accurate data for navigation and control.
Step-by-Step Power Up and Calibration
- Charge the drone battery fully.
- Attach the battery to the drone.
- Power on the drone and remote control.
- Wait for the GPS signal to lock.
- Calibrate the compass and IMU according to the manufacturer’s instructions. This usually involves performing specific movements with the drone.
- Perform a pre-flight motor test to ensure all motors spin correctly.
Connecting Drone to Remote Control
The process of connecting the drone to the remote control varies depending on the model. Generally, it involves pairing the drone and remote via Bluetooth or Wi-Fi. The specific steps are usually detailed in the user manual.
Setting Up GPS and Essential Features
Ensure the GPS signal is strong and accurate before takeoff. Some drones also allow for setting parameters such as altitude limits, return-to-home settings, and other safety features. These settings should be configured according to the flight environment and preferences.
Pre-Flight Range Test
Before flying in a critical area, perform a range test to determine the maximum reliable distance between the drone and the remote control. This helps to understand the limits of the control signal and prevents loss of control.
Essential Pre-Flight Checks (Bulleted List)
- Battery charge
- Propeller condition
- GPS signal strength
- Remote control connection
- Calibration
- Environmental conditions
- Obstacles in flight path
Flight Controls and Maneuvers
Understanding basic and advanced flight controls allows for safe and precise drone operation. This section covers fundamental maneuvers and more advanced techniques.
Basic Flight Controls
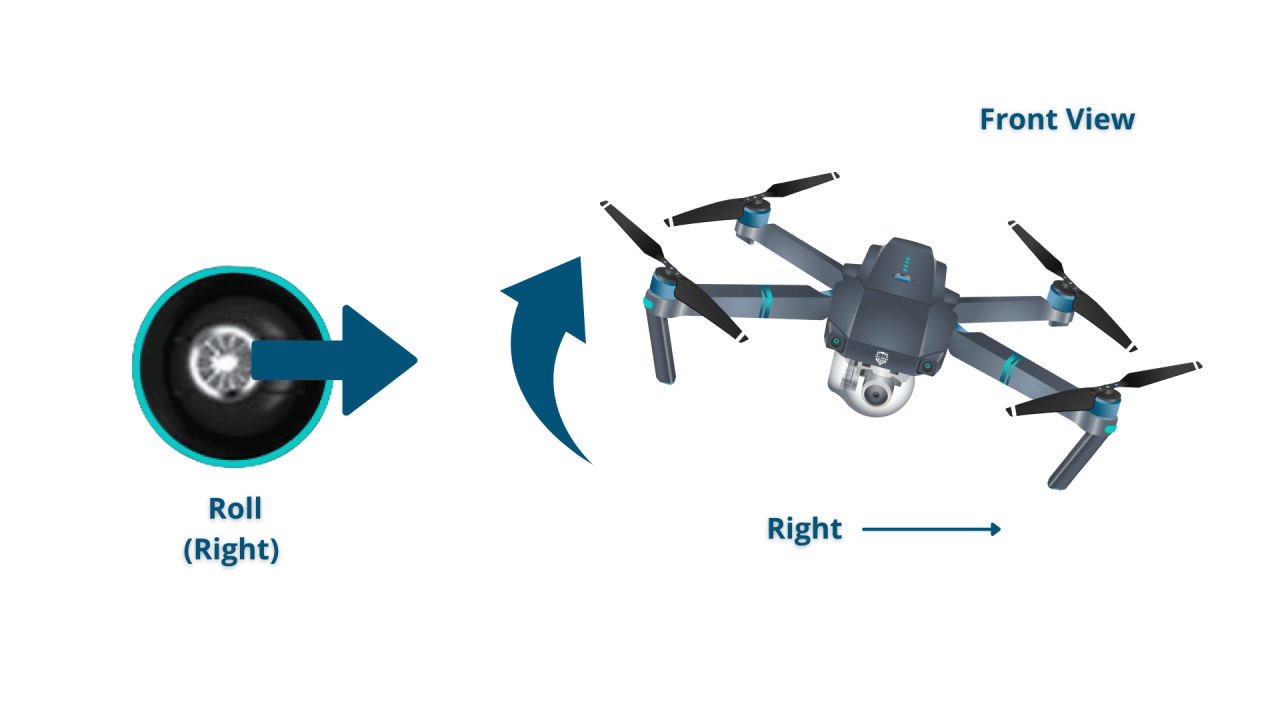
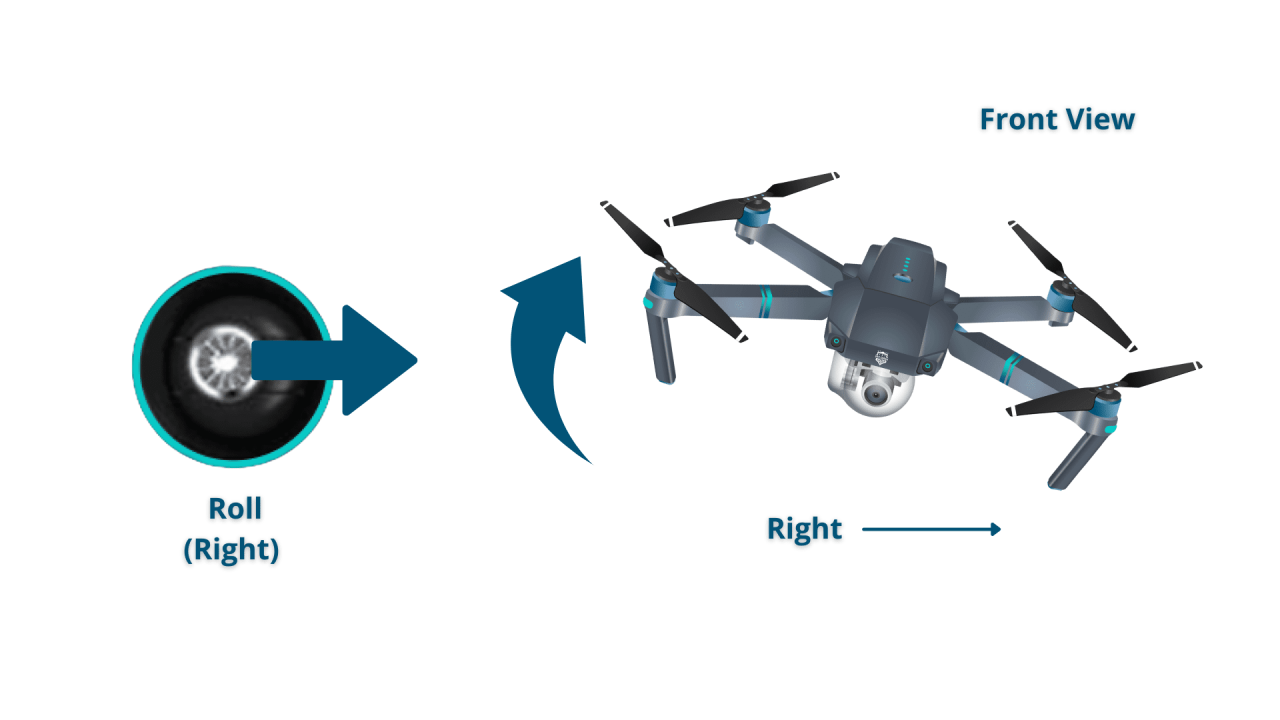
The four basic controls are throttle (altitude), pitch (forward/backward), roll (left/right), and yaw (rotation). These controls are typically mapped to joysticks or sticks on the remote control.
Basic Maneuvers
Basic maneuvers include taking off, landing, hovering, and moving in various directions. These are achieved through coordinated use of the throttle, pitch, roll, and yaw controls. Smooth and controlled movements are essential for safe operation.
Advanced Maneuvers
Advanced maneuvers, such as flips and rolls, require practice and skill. These should only be attempted in a safe and open environment away from obstacles and people. Always prioritize safety when performing advanced maneuvers.
Stable Flight in Different Weather Conditions
Maintaining stable flight in windy conditions requires adjusting the controls to compensate for wind gusts. Flying in strong winds is generally discouraged, as it can lead to loss of control or damage to the drone.
Flying in Confined Spaces (Step-by-Step Guide)
- Thoroughly assess the environment for obstacles.
- Start with slow and deliberate movements.
- Maintain a safe distance from obstacles.
- Use low speeds and precise control inputs.
- Be prepared to land immediately if necessary.
Drone Photography and Videography
Capturing stunning aerial photos and videos requires understanding camera settings, composition techniques, and post-processing. This section provides tips for enhancing your drone photography and videography skills.
Capturing High-Quality Photos and Videos
High-quality aerial photography and videography depend on factors like camera settings (aperture, shutter speed, ISO), lighting conditions, and the choice of shooting mode (photo, video, timelapse). Experiment with different settings to achieve the desired results.
Achieving Different Camera Angles and Shots
Drone cameras offer the ability to capture unique perspectives and angles. Experiment with different camera angles such as high-angle shots, low-angle shots, and cinematic sweeping shots to add visual interest to your footage.
Importance of Lighting and Composition
Good lighting is essential for high-quality images. Avoid shooting in harsh midday sun, and consider using the golden hour (sunrise and sunset) for softer, more flattering light. Composition is equally important. Utilize the rule of thirds and leading lines to create visually appealing shots.
Tips for Editing Drone Footage
Editing drone footage often involves color correction, stabilization, and adding transitions or music. Various video editing software options are available, each with different features and capabilities. Familiarize yourself with the basics of video editing to enhance your footage.
Tips for Taking Stunning Aerial Photographs (Bulleted List)
- Use the golden hour for optimal lighting.
- Experiment with different angles and perspectives.
- Pay attention to composition and framing.
- Utilize the rule of thirds.
- Edit your photos to enhance color and contrast.
Troubleshooting and Maintenance
Regular maintenance and prompt troubleshooting are crucial for extending the lifespan of your drone and ensuring its safe operation. This section provides guidance on common issues and maintenance procedures.
Common Drone Problems and Solutions, How to operate a drone
Common problems include battery issues, motor malfunctions, GPS signal loss, and camera malfunctions. Troubleshooting often involves checking connections, inspecting components for damage, and potentially replacing faulty parts. Refer to the manufacturer’s troubleshooting guide for specific solutions.
Importance of Regular Drone Maintenance

Regular maintenance extends the life of the drone and prevents potential problems during flight. This includes cleaning the drone, inspecting components for wear and tear, and lubricating moving parts.
Cleaning and Storing a Drone
Clean the drone after each flight using a soft brush and compressed air to remove dust and debris. Store the drone in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight and moisture.
Handling Minor Repairs and Seeking Professional Help
Minor repairs, such as replacing propellers or tightening screws, can often be performed at home. However, more complex repairs should be handled by qualified professionals to avoid further damage.
Routine Maintenance Schedule
| Task | Frequency | Tools Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Inspect propellers | After each flight | Visual inspection | Check for cracks, damage, or wear. |
| Clean drone body | After each flight | Soft brush, compressed air | Remove dirt and debris. |
| Check battery health | Before each flight | Battery charger, multimeter (optional) | Ensure battery is properly charged and not damaged. |
| Inspect gimbal (if applicable) | Monthly | Soft cloth | Clean and lubricate gimbal components as needed. |
Emergency Procedures
Knowing how to handle emergencies is vital for safe drone operation. This section Artikels procedures for various emergency situations.
Steps to Take If a Drone Malfunctions During Flight
If a drone malfunctions, the first priority is to ensure the safety of people and property. Attempt to regain control if possible, and if not, prepare for an emergency landing. Many drones have a return-to-home (RTH) function that can be activated.
Recovering a Crashed Drone
Carefully examine the drone for damage after a crash. Repair or replace damaged components as needed. Ensure the area is safe before attempting recovery.
Understanding how to operate a drone safely and effectively involves several key steps, from pre-flight checks to mastering the controls. Learning the basics is crucial, and a great resource for this is the comprehensive guide on how to operate a drone , which covers everything from regulations to practical flying techniques. Once you’ve grasped these fundamentals, you’ll be well on your way to confidently piloting your drone.
Dealing with Lost or Stolen Drones
Report lost or stolen drones to the authorities. If the drone has a GPS tracker, utilize it to locate the drone’s last known location. Consider registering the drone with a tracking service.
Understanding drone operation involves familiarizing yourself with its controls and safety protocols. A crucial first step is learning about pre-flight checks and maneuvering techniques, which are detailed in this comprehensive guide on how to operate a drone. Mastering these fundamentals ensures safe and efficient drone flights, ultimately leading to a more enjoyable and productive experience.
Handling Low Battery Warnings
A low battery warning should prompt an immediate return to the launch point. Never push the drone’s limits; prioritize a safe landing over completing a flight.
Emergency Procedure Flowchart (Description)
A flowchart would begin with a malfunction detection. Branches would lead to actions like attempting to regain control, activating RTH, performing an emergency landing, and contacting emergency services if necessary. Another branch would address post-crash procedures such as assessing damage and reporting the incident.
Mastering the art of drone operation requires a blend of theoretical knowledge and practical experience. By understanding drone regulations, familiarizing yourself with the technology, and practicing safe flight techniques, you can unlock the immense potential of aerial photography and videography. Remember that continuous learning and adherence to safety guidelines are paramount for a rewarding and responsible drone piloting experience.
Soar responsibly and enjoy the breathtaking perspectives that await!
Questions Often Asked: How To Operate A Drone
What type of drone is best for beginners?
For beginners, a user-friendly drone with GPS stabilization, obstacle avoidance, and return-to-home features is recommended. Look for models with intuitive controls and a good safety record.
How long does a drone battery last?
Drone battery life varies greatly depending on the drone model, battery size, and flight conditions. Expect flight times ranging from 15 to 30 minutes on a single charge. Always carry extra batteries.
What should I do if I lose control of my drone?
If you lose control, immediately try to regain control using the emergency stop function if available. If that fails, activate the return-to-home function (if equipped). If the drone is unresponsive, contact local authorities if it poses a safety hazard.
How do I obtain a drone license or permit?
Drone regulations vary by country and region. Check with your local aviation authority to determine the specific licensing or registration requirements for operating drones in your area.